The explosion risk in industrial settings jumps dramatically when electrical equipment operates in volatile environments. Why? Because nearby hazardous materials and gases become additional fuel sources, turning a small incident into something much worse.
Facilities handling RCRA hazardous waste know this danger firsthand. These materials often have ignitable properties – even a small spark can kick off serious trouble. I’ve seen situations where seemingly minor electrical issues created major safety concerns.
NEMA 7 enclosures came about because of these real-world hazards. They’ve saved countless industrial operations from devastating incidents by establishing practical safety measures for electrical components in dangerous areas. Looking at these specialized containers helps us understand proper protection in hazardous settings.
What Is a NEMA 7 Enclosure?
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) developed various standards for electrical enclosures based on environmental conditions. Their NEMA 7 classification specifically addresses explosion concerns in what safety regulations designate as Class I, Division 1 hazardous areas – locations where you’ll regularly find flammable gases or vapors during normal operations.
These aren’t just tough boxes. NEMA 7 enclosures actually trap explosions before they can spread. Rather than building something that might withstand a blast, engineers created containment systems that keep the explosion confined to the enclosure itself, preventing ignition of the surrounding atmosphere. This containment approach works much better than simply trying to build stronger equipment.
Key Features of NEMA 7 Enclosures
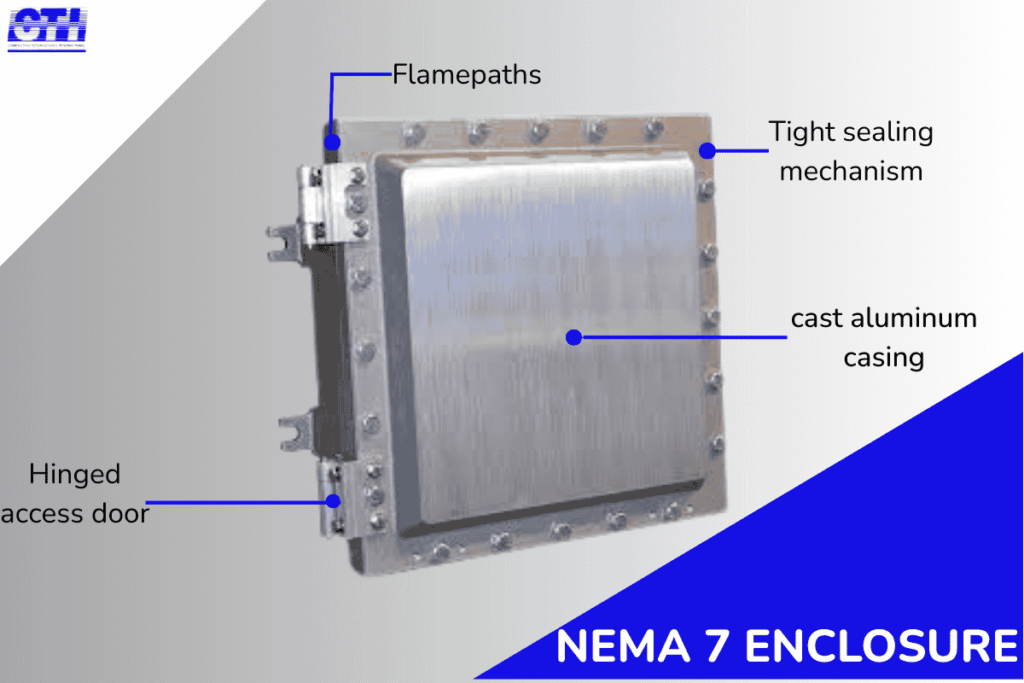
NEMA 7 enclosures have specifications that make them what they are and give them their abilities. These key features typically include:
- A cast metal construction (usually aluminum or iron)
- Precision-machined flamepaths (or flame joints)
- Extra-thick walls to contain pressure
- Cooling fins for heat dispersion
- Specialized sealing mechanisms
Engineers design these enclosures with “flame paths” which are specific gaps allowing explosion pressure to escape while cooling gases below ignition temperature before they exit the container.
Where Are NEMA 7 Enclosures Used?
Several industries rely on NEMA 7 enclosures to maintain safety standards, among the list of common industries are:
Oil and Gas Facilities
The electrical equipment used in oil and gas refineries and processing plants are at high risk of igniting the surrounding flammable hydrocarbons. They require more advanced protection in the event of an explosion.
Chemical Manufacturing
There are so many flammable chemicals. Facilities producing solvents, fuels, and other volatile compounds like paint will need NEMA 7 enclosures for their switches, junction boxes, and control panels.
Pharmaceutical Production
An industry that needs to be constantly monitored is the pharmaceutical sector. Many processes here involve the presence and use of flammable solvents which have the ability to aggravate the effects of an explosion. For this reason, electrical protection is required here too.
Hazardous Waste Manufacturing
Sites that create or manage hazardous waste must implement appropriate containment for electrical equipment. This includes industrial facilities such as aerospace, biomedical, and manufacturing industries handling hazardous or radioactive waste. It is recommended to use suitable compactors for the wastes and NEMA 7 protection for the electrical components.
NEMA 7 vs Other NEMA Ratings
NEMA has developed ratings addressing various environmental challenges. They are not in a competition or updates of themselves, but rather standards for different sectors. NEMA 4 focuses on water protection, NEMA 12 guards against dust, while NEMA 7 specifically handles explosion hazards. Facility managers must understand these differences when selecting appropriate protection.
NEMA Enclosure Ratings: Complete Classification Guide
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) ratings define the types of environments where electrical enclosures can be safely used. This table explains the key NEMA ratings, their protection levels, and typical applications.
| NEMA Rating | Protection Level | Environmental Protection | Typical Applications |
| NEMA 1 | Indoor, General Purpose | Basic protection against dust, light, and indirect splashing | Office environments, control panels in non-hazardous indoor locations |
| NEMA 2 | Indoor, Drip-Proof | Protection against limited amounts of falling water and light dripping | Indoor installations where condensation may be present |
| NEMA 3 | Outdoor, Weather-Resistant | Protection against windblown dust, rain, sleet, and external ice formation | Outdoor equipment, roadside installations |
| NEMA 3R | Outdoor, Rainproof | Protection against falling rain and external ice formation | Outdoor electrical installations, utility connections |
| NEMA 3S | Outdoor, Sleet-Resistant | Same as NEMA 3 plus protection from sleet damage to external mechanisms | Traffic controls, outdoor equipment in northern climates |
| NEMA 4 | Indoor/Outdoor, Watertight | Protection against windblown dust, rain, splashing water, and hose-directed water | Food processing areas, dairies, breweries, wastewater facilities |
| NEMA 4X | Indoor/Outdoor, Watertight and Corrosion-Resistant | Same as NEMA 4 plus corrosion resistance | Chemical plants, marine environments, food processing, wastewater treatment |
| NEMA 5 | Indoor, Dust-Tight | Protection against settling dust, falling dirt, and dripping non-corrosive liquids | Manufacturing areas with high airborne particle content |
| NEMA 6 | Indoor/Outdoor, Submersible | Protection against temporary submersion at limited depth | Locations subject to occasional submersion, pump pits, flood-prone areas |
| NEMA 6P | Indoor/Outdoor, Prolonged Submersion | Protection against prolonged submersion at limited depth | Underground pits, below-grade installations subject to prolonged flooding |
| NEMA 7 | Indoor, Hazardous Locations Class I | Protection against explosive gases, vapors (contains internal explosions) | Oil refineries, fuel storage facilities, paint booths, hazardous waste handling |
| NEMA 8 | Indoor/Outdoor, Hazardous Locations Class I | Same as NEMA 7 but for indoor or outdoor use | Oil fields, fuel transfer stations, chemical processing areas |
| NEMA 9 | Indoor, Hazardous Locations Class II | Protection against combustible dust | Grain processing, flour storage, coal handling, metal powder processing |
| NEMA 10 | Mining (MSHA) | Built to Mine Safety and Health Administration requirements | Underground mining operations |
| NEMA 12 | Indoor, Industrial Use | Protection against dust, falling dirt, and dripping non-corrosive liquids | General industrial applications, most manufacturing floors |
| NEMA 13 | Indoor, Oil and Dust Protection | Protection against dust, spraying water, oil, and coolant | Machine tool areas, automotive manufacturing, metalworking facilities |
Regulatory Compliance and NEMA 7
Selecting correct electrical enclosures fulfills important regulatory requirements:
- OSHA mandates specific electrical equipment for hazardous locations
- The National Electric Code (NEC) classifies hazardous areas and requires appropriate protection
- Facilities handling household hazardous waste must follow location-specific electrical classifications
Failing to comply creates safety risks and can result in penalties, facility closures, and liability issues after incidents.
Installation Considerations for NEMA 7 Enclosures
Installing these specialized NEMA 7 enclosures requires technical expertise and knowledge of the policies.
Here are the specifications to be implemented::
- All conduit entries must maintain explosion-proof integrity
- Boundary crossings need proper sealing fittings
- Regular inspection schedules ensure continued protection
- Only qualified professionals should perform installations
Many facilities work with safety consultants to implement explosion-proof systems correctly within their waste management infrastructure.
The Real Cost of NEMA 7 Protection
NEMA 7 enclosures cost more than standard electrical boxes initially, but this investment prevents potentially catastrophic expenses. So, the real cost of NEMA 7 protection is what it prevents.
Some issues that NEMA 7 enclosures could prevent from a single explosion include:
- Extensive equipment damage
- Production losses from downtime
- Worker injuries
- Regulatory fines
- Insurance increases
For facilities handling volatile materials or RCRA hazardous waste, these enclosures represent necessary protection, not optional upgrades.
Improving Your Hazardous Waste Management
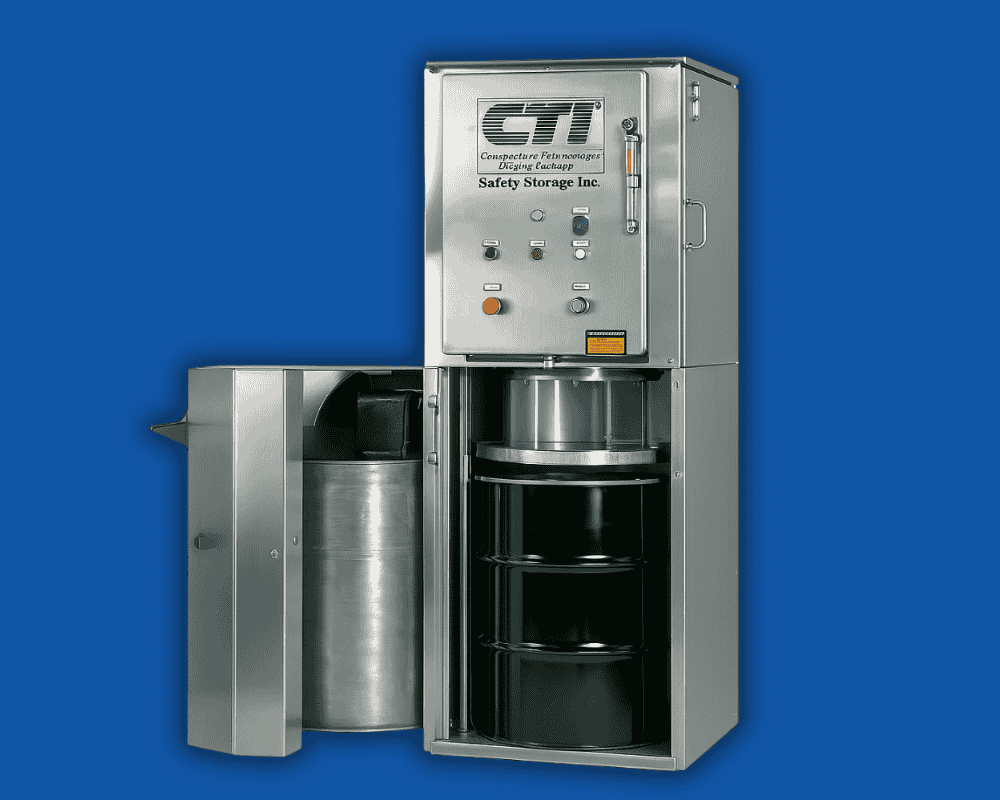

Electrical safety forms just one part of effective hazardous waste management. CTI Safe Storage offers industrial waste compactors designed specifically for hazardous waste environments to complement your safety measures.
Our compactors reduce waste volume while maintaining strict safety standards for facilities handling flammable materials. Combining proper electrical protection through NEMA 7 enclosures with our volume-reducing equipment helps your facility achieve both safety compliance and operational efficiency.
Contact a waste compactor manufacturer today to see how industrial compactors integrate with your safety protocols while reducing disposal costs and enhancing your environmental program.
Ensure NEMA 7 in Your Facility
NEMA 7 enclosures are essential security measures for all facilities, especially for those that have hazardous gases in their environment. Facility managers who understand their function, applications, and importance make better decisions about electrical system protection in hazardous environments. When paired with comprehensive waste management strategies, these specialized enclosures create safer workplaces while maintaining regulatory compliance.
From chemical plants to university research facilities, proper electrical protection creates fundamentally safer environments where potential incidents remain contained and controlled.




